The Earth’s Great Spheres
Lithosphere- The lithosphere contains all of the cold, hard solid land of the planet’s crust (surface), the semi-solid land underneath the crust, and the liquid land near the center of the planet
Hydrosphere- The hydrosphere contains all the solid, liquid, and gaseous water of the plane
Biosphere– The biosphere contains all the planet’s living things. This sphere includes all of the microorganisms, plants, and animals of Ear
Atmosphere- The atmosphere contains all the air in Earth’s system
The Earth’s Great Spheres
Lithosphere– The lithosphere contains all of the cold, hard solid land of the planet’s crust (surface), the semi-solid land underneath the crust, and the liquid land near the center of the planet
Hydrosphere– The hydrosphere contains all the solid, liquid, and gaseous water of the plane
| People and Environment- Pollutants | |
| Biodegradable and Non Bio Degradable Pollutants | |
| Agents of Pollution | |
| Effects of Pollution | |
| Atmosphere and Air pollution | |
| Primary and secondary Air Pollutants | |
| Pollution and their effect on Human being | |
| Environment MCQs | |
| Light Pollution and effects and Steps taken |
Biosphere– The biosphere contains all the planet’s living things. This sphere includes all of the microorganisms, plants, and animals of Ear
Atmosphere- The atmosphere contains all the air in Earth’s system
Primary Air Pollutants
Five major materials released directly into the atmosphere in unmodified forms.
-Carbon monoxide
-Sulfur dioxide
-Nitrogen oxides
-Hydrocarbons
-Particulate matter
Carbon Monoxide
- Produced by burning of organic material (coal, gas, wood, trash, etc.)
- Cigarette smoke another major source
- Toxic because binds to hemoglobin, reduces oxygen in blood
- Not a persistent pollutant, combines with oxygen to form CO2
Sulphur Dioxide
- Produced by burning sulfur containing fossil fuels (coal, oil)
- Coal-burning power plants major source
- Reacts in atmosphere to produce acids
London
–1306 banned burning of sea coal
-1952 “killer fog”: 4,000 people died in 4 weeks
tied to sulfur compounds in smog
Nitrogen Oxides
Produced from burning of fossil fuels
Contributes to acid rain, smog
Automobile engine main source
Hydrocarbons
- Hydrocarbons – organic compounds with hydrogen, carbon
- From incomplete burning or evaporated from fuel supplies
- Major source is automobiles, but some from industry
- Contribute to smog
- Improvements in engine design have helped reduce
Secondary Pollutants
- Ozone
- PAN (peroxy acetyl nitrate)
- Photochemical smog
- Aerosols and mists (H2SO4)
Ozone
Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive gas composed of three oxygen atoms.
It is both a natural and a man-made product that occurs in the Earth’s upper atmosphere (the stratosphere) and lower atmosphere (the troposphere).
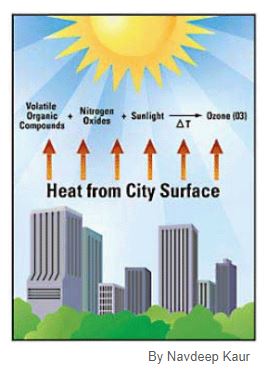
Tropospheric ozone – what we breathe — is formed primarily from photochemical reactions between two major classes of air pollutants, volatile organic compounds (VOC) and nitrogen oxides (NOX).
Volatile organic compounds, sometimes referred to as VOCs, are organic compounds that easily become vapors or gases. Along with carbon, they contain elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, sulfur or nitrogen.
Smog is caused by the interaction of some hydrocarbons and oxidants under the influence of sunlight giving rise to dangerous peroxy acetyl nitrate (PAN).
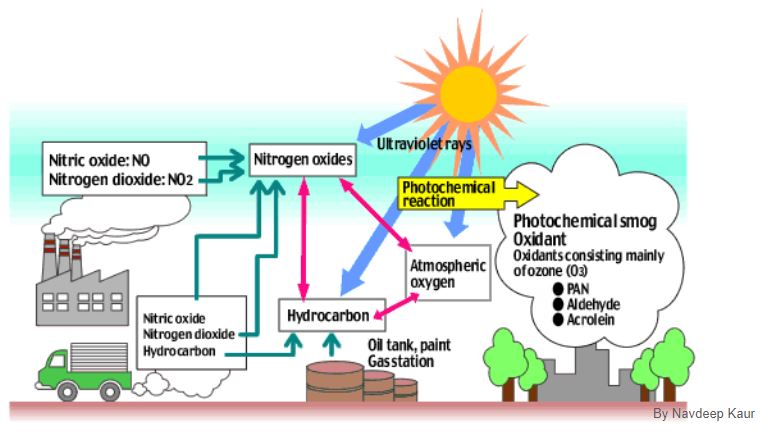
Photochemical smog
Photochemical smog is a mixture of pollutants which includes particulates, nitrogen oxides, ozone, aldehydes, peroxyethanoyl nitrate (PAN), unreacted hydrocarbons, etc. The smog often has a brown haze due to the presence of nitrogen dioxide. It causes painful eyes.
World Energy Conservation Day 14 November
World Tiger Day 29 July
National Pollution prevention day 2nd December is observed as National Pollution Prevention Day in India. This day is observed in the memory of people who lost their lives in Bhopal gas calamity. Bhopal gas tragedy occurred in the year 1984 on the night of 2–3 December.
World energy day 14 Dec
International Biodiversity day 22 may






