- Quiz will start as soon as you click the ‘Start Quiz‘ button below.
- Question will come one by one click on next for next question
- There are 30 questions in this quiz, you will get 30 Minutes to attempt.
- 2 Marks is determined for the correct answer for each question. There is no negative marking for incorrect answer.
- After the quiz is over, in order to know your rank in the Ranking List / Leader-board below, you should enter your name and email address, otherwise you will be deprived of it.
- After completing click on finish Quiz
- To see correct answers click on view Question
- जैसे ही आप नीचे दिए गए ‘स्टार्ट क्विज़’ बटन पर क्लिक करेंगे, क्विज़ शुरू हो जाएगा।
प्रश्न अगले प्रश्न के लिए अगले एक क्लिक पर आएगा
इस क्विज में 30 प्रश्न हैं, आपको प्रयास करने के लिए 30 मिनट मिलेंगे।
प्रत्येक प्रश्न के सही उत्तर के लिए 2 अंक निर्धारित किए गए हैं। गलत उत्तर के लिए कोई नकारात्मक अंकन नहीं है।
प्रश्नोत्तरी समाप्त होने के बाद, नीचे दी गई रैंकिंग सूची / लीडर-बोर्ड में अपनी रैंक जानने के लिए, आपको अपना नाम और ईमेल पता दर्ज करना चाहिए, अन्यथा आप इससे वंचित रह जाएंगे।
फिनिश क्विज़ पर क्लिक करने के बाद
सही उत्तर देखने के लिए प्रश्न पर क्लिक करें
Paper 2 CS System Software & Operating System Part 1
Quiz-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
Paper 1 Quiz helps u to Excel in NET JRF
Paper 1 All questions 2 Marks each
- Navdeep Kaur
- All the Best
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
Average marks Improve next time All the Best
-
Nice Keep it up, Stay Blessed
-
Awesome Great Marks, Keep doing
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
2 pointsA critical section is a program segment
Correct
In concurrent programming, concurrent accesses to shared resources can lead to unexpected or erroneous behavior, so parts of the program where the shared resource is accessed are protected. This protected section is the critical section .
Incorrect
In concurrent programming, concurrent accesses to shared resources can lead to unexpected or erroneous behavior, so parts of the program where the shared resource is accessed are protected. This protected section is the critical section .
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
2 pointsIn which of the following four necessary conditions for deadlock processes claim exclusive control of the resources they require?
Correct
Mutual Exclusion is a condition when one or more than one resource are non-sharable (Only one process can use at a time) i.e. processes claim exclusive control of the resources they require.
Incorrect
Mutual Exclusion is a condition when one or more than one resource are non-sharable (Only one process can use at a time) i.e. processes claim exclusive control of the resources they require.
-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
2 pointsFork is
Correct
“fork() creates a new process by duplicating the calling process, The new process, referred to as child, is an exact duplicate of the calling process, referred to as parent, except for the following :
The child has its own unique process ID, and this PID does not match the ID of any existing process group.
The child’s parent process ID is the same as the parent process ID.
The child does not inherit its parent’s memory locks and semaphore
adjustments.
The child does not inherit outstanding asynchronous I/O operations from its parent nor does it inherit any asynchronous I/O contexts from its parent.”Incorrect
“fork() creates a new process by duplicating the calling process, The new process, referred to as child, is an exact duplicate of the calling process, referred to as parent, except for the following :
The child has its own unique process ID, and this PID does not match the ID of any existing process group.
The child’s parent process ID is the same as the parent process ID.
The child does not inherit its parent’s memory locks and semaphore
adjustments.
The child does not inherit outstanding asynchronous I/O operations from its parent nor does it inherit any asynchronous I/O contexts from its parent.” -
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following need not necessarily be saved on a Context Switch between processes?
Correct
“The values stored in registers, stack pointers and program counters are saved on context switch between the processes so as to resume the execution of the process.
There’s no need of saving the contents of TLB as it is invalidated after each context switch.”Incorrect
“The values stored in registers, stack pointers and program counters are saved on context switch between the processes so as to resume the execution of the process.
There’s no need of saving the contents of TLB as it is invalidated after each context switch.” -
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
2 pointsAt a particular time, the value of a counting semaphore is 10, it will become 7 after: (a) 3 V operations (b) 3 P operations (c) 5 V operations and 2 P operations (d) 2 V operations and 5 P operations Which of the following option is correct?
Correct
“P: Wait operation decrements the value of the counting semaphore by 1.
V: Signal operation increments the value of counting semaphore by 1.
Current value of the counting semaphore = 10
a) after 3 P operations, value of semaphore = 10-3 = 7
d) after 2 v operations, and 5 operations value of semaphore = 10 + 2 – 5 = 7
“Incorrect
“P: Wait operation decrements the value of the counting semaphore by 1.
V: Signal operation increments the value of counting semaphore by 1.
Current value of the counting semaphore = 10
a) after 3 P operations, value of semaphore = 10-3 = 7
d) after 2 v operations, and 5 operations value of semaphore = 10 + 2 – 5 = 7
“ -
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
2 pointsConsider a logical address space of 8 pages of 1024 words mapped into memory of 32 frames.
How many bits are there in the logical address?Correct
“logical address space = 8 pages of 1024 words
number of bits in logical address space = p (page bits) + d (offset bits)
number of bits = log28 + log21024 = 3 + 10 = 13 bits”Incorrect
“logical address space = 8 pages of 1024 words
number of bits in logical address space = p (page bits) + d (offset bits)
number of bits = log28 + log21024 = 3 + 10 = 13 bits” -
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
2 pointsThe performance of Round Robin algorithm depends heavily on
Correct
“In Round Robin algorithm, it is very important to choose the the quantum carefully as smaller time quanta leads to more context switches thereby reducing the efficiency of the CPU and the larger time quanta makes the round robin algorithm regenerate into FCFS algorithm.
“Incorrect
“In Round Robin algorithm, it is very important to choose the the quantum carefully as smaller time quanta leads to more context switches thereby reducing the efficiency of the CPU and the larger time quanta makes the round robin algorithm regenerate into FCFS algorithm.
“ -
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
2 pointsThe performance of Round Robin algorithm depends heavily on
Correct
“In Round Robin algorithm, it is very important to choose the the quantum carefully as smaller time quanta leads to more context switches thereby reducing the efficiency of the CPU and the larger time quanta makes the round robin algorithm regenerate into FCFS algorithm.
“Incorrect
“In Round Robin algorithm, it is very important to choose the the quantum carefully as smaller time quanta leads to more context switches thereby reducing the efficiency of the CPU and the larger time quanta makes the round robin algorithm regenerate into FCFS algorithm.
“ -
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
2 pointsThe page replacement algorithm which gives the lowest page fault rate is
Correct
In Optimal Page replacement algorithm, pages are replaced which are not used for the longest duration of time in the future. This page replacement algorithm ensures the lowest page fault rate.
Incorrect
In Optimal Page replacement algorithm, pages are replaced which are not used for the longest duration of time in the future. This page replacement algorithm ensures the lowest page fault rate.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
2 pointsThe primary purpose of an operating system is
Correct
“Explanation: An operating system has three main functions:
(1) manage the computer’s resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, and other input – output sources
(2) establish a user interface, and
(3) execute and provide services for applications software.
OS provides an interface between the user and the hardware and thus making the computer easy to use for the user but the primary function of OS is to manage the hardware in the most efficient way.
“Incorrect
“Explanation: An operating system has three main functions:
(1) manage the computer’s resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, and other input – output sources
(2) establish a user interface, and
(3) execute and provide services for applications software.
OS provides an interface between the user and the hardware and thus making the computer easy to use for the user but the primary function of OS is to manage the hardware in the most efficient way.
“ -
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
2 pointsWhich is the correct definition of a valid process transition in an operating system?
Correct
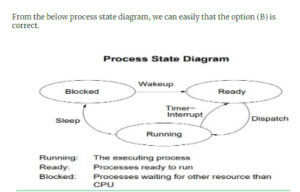 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
2 points“The correct matching of the following pairs is
(A) Disk check (1) Round robin
(B) Batch processing (2) Scan
(C) Time sharing (3) LIFO
(D) Stack operation (4) FIFO”Correct
“Scan is disk scheduling algorithm
In the round robin algorithm, each process will execute for particular time quantum,So it is the example for time sharing,
Stack is last in first out(LIFO)
In the batching processing, whatever process arrives first, it execute that process. So it First in First out(FIFO)”Incorrect
“Scan is disk scheduling algorithm
In the round robin algorithm, each process will execute for particular time quantum,So it is the example for time sharing,
Stack is last in first out(LIFO)
In the batching processing, whatever process arrives first, it execute that process. So it First in First out(FIFO)” -
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
2 pointsA page fault
Correct
A page fault is a type of exception raised by computer hardware when a running program accesses a memory page that is not currently mapped by the memory management unit (MMU) into the virtual address space of a process
Incorrect
A page fault is a type of exception raised by computer hardware when a running program accesses a memory page that is not currently mapped by the memory management unit (MMU) into the virtual address space of a process
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
2 pointsLet the page fault service time be 10 ms in a computer with average memory access time being 20 ns. If the one-page fault is generated for every 106 memory accesses, what is the effective access time for the memory?
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
2 pointsConsider a system having “n” resources of same type. These resources are shared by 3 processes, A, B, C. These have peak demands of 3, 4, and 6 respectively. For what value of “n” deadlock won’t occur
Correct
Number of min resources required = (3-1) + (4-1) + (6-1) + 1 = 11
Incorrect
Number of min resources required = (3-1) + (4-1) + (6-1) + 1 = 11
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
2 points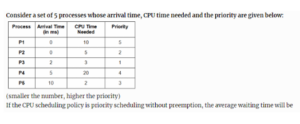 Correct
Correct
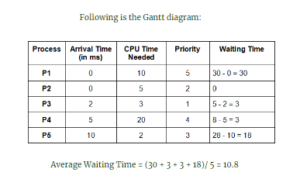 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
2 pointsWith single resource, deadlock occurs
Correct
Only Single resource available never occur deadlock because it violates circular wait and hold & wait condition.
Incorrect
Only Single resource available never occur deadlock because it violates circular wait and hold & wait condition.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
2 pointsAt a particular time of computation the value of a counting semaphore is 7. Then 20 P operations and xV operations were completed on this semaphore. If the new value of semaphore is 5 ,x will be
Correct
“Here, 20P operations means 20 wait operations. It decrement value by 1 every time.
xV operations means x increments operations. It increment value by 1 every time.
→ New value of semaphore is 5 after performing xV operations
= -13 + xV
= 5
xV = 5 + 13
= 18
→ After applying 20P operations in semaphore value is = 7-20 = -13
“Incorrect
“Here, 20P operations means 20 wait operations. It decrement value by 1 every time.
xV operations means x increments operations. It increment value by 1 every time.
→ New value of semaphore is 5 after performing xV operations
= -13 + xV
= 5
xV = 5 + 13
= 18
→ After applying 20P operations in semaphore value is = 7-20 = -13
“ -
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
2 pointsA system has 3 processes sharing 4 resources. If each process needs a maximum of 2 units, then
Correct
If the system is deadlocked, it implies that each process is holding one resource and is waiting for one more. Since there are 3 processes and 4 resources, one process must be able to obtain two resources. This process requires no more resources and therefore it will return its resources when done.
Incorrect
If the system is deadlocked, it implies that each process is holding one resource and is waiting for one more. Since there are 3 processes and 4 resources, one process must be able to obtain two resources. This process requires no more resources and therefore it will return its resources when done.
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
2 pointsDetermine the number of page faults when references to pages occur in the following order: 1, 2, 4, 5, 2, 1, 2, 4 Assume that the main memory can accommodate 3 pages and the main memory already has the pages 1 and 2, with page one having brought earlier than page 2. (LRU page replacement algorithm is used)
Correct
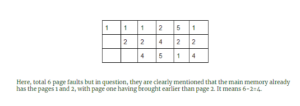 Incorrect
Incorrect
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
2 pointsWorking Set(t,k) at an instant of time t is
Correct
“→ Working set defines the amount of memory that a process requires in a given time interval.
→ It defines “the working set of information W(t,τ) of a process at time t to be the collection of information referenced by the process during the process time interval (t−τ,t)”.
→ Typically the units of information in question are considered to be memory pages. This is suggested to be an approximation of the set of pages that the process will access in the future (say during the next τ time units), and more specifically is suggested to be an indication of what pages ought to be kept in main memory to allow most progress to be made in the execution of that process.
“Incorrect
“→ Working set defines the amount of memory that a process requires in a given time interval.
→ It defines “the working set of information W(t,τ) of a process at time t to be the collection of information referenced by the process during the process time interval (t−τ,t)”.
→ Typically the units of information in question are considered to be memory pages. This is suggested to be an approximation of the set of pages that the process will access in the future (say during the next τ time units), and more specifically is suggested to be an indication of what pages ought to be kept in main memory to allow most progress to be made in the execution of that process.
“ -
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
2 pointsA CPU generates 32-bit virtual addresses. The page size is 4 KB. The processor has a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which can hold a total of 128 page table entries and is 4-way set associative. The minimum size of the TLB tag is:
Correct
“Page size = 4 KB = 4 × 210 Bytes = 212 Bytes
Virtual Address = 32 bit
No. of bits needed to address the page frame = 32 – 12 = 20
TLB can hold 128 page table entries with 4-way set associative
⇒ 128/4=32=25
→ 5 bits are needed to address a set.
→ The size of TLB tag = 20 – 5 = 15 bits
“Incorrect
“Page size = 4 KB = 4 × 210 Bytes = 212 Bytes
Virtual Address = 32 bit
No. of bits needed to address the page frame = 32 – 12 = 20
TLB can hold 128 page table entries with 4-way set associative
⇒ 128/4=32=25
→ 5 bits are needed to address a set.
→ The size of TLB tag = 20 – 5 = 15 bits
“ -
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
2 pointsFor the real time operating system, which of the following is the most suitable scheduling scheme?
Correct
“→ Preemption is the act of temporarily interrupting a task being carried out by a computer system, without requiring its cooperation, and with the intention of resuming the task at a later time. Such changes of the executed task are known as context switches.
→ It is normally carried out by a privileged task or part of the system known as a preemptive scheduler, which has the power to preempt, or interrupt, and later resume, other tasks in the system.
→ Preemptive scheduling is the most suitable scheduling scheme for real time operating systems as it can always preempt other processes based on priority.
→ In real time operating systems, we have different tasks to perform simultaneously and also there are a few tasks which need to be performed first at priority basis.
“Incorrect
“→ Preemption is the act of temporarily interrupting a task being carried out by a computer system, without requiring its cooperation, and with the intention of resuming the task at a later time. Such changes of the executed task are known as context switches.
→ It is normally carried out by a privileged task or part of the system known as a preemptive scheduler, which has the power to preempt, or interrupt, and later resume, other tasks in the system.
→ Preemptive scheduling is the most suitable scheduling scheme for real time operating systems as it can always preempt other processes based on priority.
→ In real time operating systems, we have different tasks to perform simultaneously and also there are a few tasks which need to be performed first at priority basis.
“ -
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
2 pointsIn which one of the page replacement policies, Belady’s anomaly may occur?
Correct
“→ Belady’s anomaly is the phenomenon in which increasing the number of page frames results in an increase in the number of page faults for certain memory access patterns.
→ This phenomenon is commonly experienced when using the first-in first-out (FIFO) page replacement algorithm.
→ In FIFO, the page fault may or may not increase as the page frames increase, but in Optimal and stack-based algorithms like LRU, as the page frames increase the page fault decreases.
“Incorrect
“→ Belady’s anomaly is the phenomenon in which increasing the number of page frames results in an increase in the number of page faults for certain memory access patterns.
→ This phenomenon is commonly experienced when using the first-in first-out (FIFO) page replacement algorithm.
→ In FIFO, the page fault may or may not increase as the page frames increase, but in Optimal and stack-based algorithms like LRU, as the page frames increase the page fault decreases.
“ -
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
2 pointsSpecial software to create a job queue is called a
Correct
“Spooling is a specialized form of multi-programming for the purpose of copying data between different devices.
A dedicated program, the spooler, maintains an orderly sequence of jobs for the peripheral and feeds it data at its own rate
Conversely, for slow input peripherals, such as a card reader, a spooler can maintain a sequence of computational jobs waiting for data, starting each job when all of the relevant input is available
“Incorrect
“Spooling is a specialized form of multi-programming for the purpose of copying data between different devices.
A dedicated program, the spooler, maintains an orderly sequence of jobs for the peripheral and feeds it data at its own rate
Conversely, for slow input peripherals, such as a card reader, a spooler can maintain a sequence of computational jobs waiting for data, starting each job when all of the relevant input is available
“ -
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
2 pointsProcess is:
Correct
“A process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many threads. It contains the program code and its activity.
Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently”Incorrect
“A process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many threads. It contains the program code and its activity.
Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently” -
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
2 pointsConsider three CPU-intensive processes, which require 10, 20 and 30 time units and arrive at times 0, 2 and 6, respectively. How many context switches are needed if the operating system implements a shortest remaining time first scheduling algorithm? Do not count the context switches at time zero and at the end.
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
2 pointsUsing a larger block size in a fixed block size file system leads to
Correct
“→ While using a larger block size means that contains less number of blocks then that results better throughput.
→ This can be implemented in a fixed block size then the space utilization is not upto the mark. So the statement results better disk throughput but poorer disk space utilization
“Incorrect
“→ While using a larger block size means that contains less number of blocks then that results better throughput.
→ This can be implemented in a fixed block size then the space utilization is not upto the mark. So the statement results better disk throughput but poorer disk space utilization
“ -
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
2 pointsWhen a process is rolled back as a result of deadlock the difficulty which arises is
Correct
“→ When a process is rolled back as a result of deadlock the difficulty which arises is starvation.
→ Resource starvation is a problem encountered in concurrent computing where a process is perpetually denied necessary resources to process its work.
→ Starvation may be caused by errors in a scheduling or mutual exclusion algorithm, but can also be caused by resource leaks, and can be intentionally caused via a denial-of-service attack such as a fork bomb
“Incorrect
“→ When a process is rolled back as a result of deadlock the difficulty which arises is starvation.
→ Resource starvation is a problem encountered in concurrent computing where a process is perpetually denied necessary resources to process its work.
→ Starvation may be caused by errors in a scheduling or mutual exclusion algorithm, but can also be caused by resource leaks, and can be intentionally caused via a denial-of-service attack such as a fork bomb
“ -
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
2 pointsIf the page size in a 32-bit machine is 4K bytes then the size of the page table is
Correct
“→Page size is total space taken up by page and Page table entry size is memory taken for indexing the Page in Page Table
→Size of logical address = 32 bits
→Page size = 4K =22210=212 Bytes
→Number of pages = logical address space/ size of each page = 232/ 212= 220
→Page table size = number of pages * size of a page table entry
= 220 * 22
= 222
“Incorrect
“→Page size is total space taken up by page and Page table entry size is memory taken for indexing the Page in Page Table
→Size of logical address = 32 bits
→Page size = 4K =22210=212 Bytes
→Number of pages = logical address space/ size of each page = 232/ 212= 220
→Page table size = number of pages * size of a page table entry
= 220 * 22
= 222
“
- Next Quiz Daily at navclasses.in 12 PM
- Commerce Paper 2 Sunday at navclasses.in
- Computer Science Paper 2 Sunday at navclasses.in
- Economics Paper 2 Sunday at navclasses.in
- Education Paper 2 Sunday at navclasses.in
Study Paper 1 Topics for Free Click Here
Get subscription for Complete Preparation NTA NET JRF: https://unacademy.com/subscribe/TEWDQ
use my referral code for 10% additional discount: NAVCLASSES
Search Navdeep Kaur and start watching ongoing courses
NTA NET Paper 1
Leaderboard: Paper 2 CS System Software & Operating System Part 1
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||






