- Quiz will start as soon as you click the ‘Start Quiz‘ button below.
- Question will come one by one click on next for next question
- There are 30 questions in this quiz, you will get 30 Minutes to attempt.
- 2 Marks is determined for the correct answer for each question. There is no negative marking for incorrect answer.
- After the quiz is over, in order to know your rank in the Ranking List / Leader-board below, you should enter your name and email address, otherwise you will be deprived of it.
- After completing click on finish Quiz
- To see correct answers click on view Question
- जैसे ही आप नीचे दिए गए ‘स्टार्ट क्विज़’ बटन पर क्लिक करेंगे, क्विज़ शुरू हो जाएगा।
प्रश्न अगले प्रश्न के लिए अगले एक क्लिक पर आएगा
इस क्विज में 30 प्रश्न हैं, आपको प्रयास करने के लिए 30 मिनट मिलेंगे।
प्रत्येक प्रश्न के सही उत्तर के लिए 2 अंक निर्धारित किए गए हैं। गलत उत्तर के लिए कोई नकारात्मक अंकन नहीं है।
प्रश्नोत्तरी समाप्त होने के बाद, नीचे दी गई रैंकिंग सूची / लीडर-बोर्ड में अपनी रैंक जानने के लिए, आपको अपना नाम और ईमेल पता दर्ज करना चाहिए, अन्यथा आप इससे वंचित रह जाएंगे।
फिनिश क्विज़ पर क्लिक करने के बाद
सही उत्तर देखने के लिए प्रश्न पर क्लिक करें
Paper 2 CS Discrete Structures and Optimization Part 6
Quiz-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
Paper 1 Quiz helps u to Excel in NET JRF
Paper 1 All questions 2 Marks each
- Navdeep Kaur
- All the Best
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
Average marks Improve next time All the Best
-
Nice Keep it up, Stay Blessed
-
Awesome Great Marks, Keep doing
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
2 pointsLet L be a lattice. Then for every a and b in L which one of the following is correct?
Correct
“Distributive lattice is satisfies this condition aV(bVc)=(aVb)Vc
A distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other. “Incorrect
“Distributive lattice is satisfies this condition aV(bVc)=(aVb)Vc
A distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other. “ -
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
2 pointsIf A and B are sets and AUB = A∩B, then which of the following is correct?
Correct
“For this let x belongs to A implies x belongs to A U B
= x belongs to A intersection B
= x belongs to A and x Belongs to B
= x belongs to B
so A subset of B — (2)
Now we will let y belong to B which implies y belongs to A U B
= y belongs to A intersection B
= y belongs to A and y belongs to B
= y belongs to A
Therefore, B subset of A — (3) from (2) and (3) we get A=B. “Incorrect
“For this let x belongs to A implies x belongs to A U B
= x belongs to A intersection B
= x belongs to A and x Belongs to B
= x belongs to B
so A subset of B — (2)
Now we will let y belong to B which implies y belongs to A U B
= y belongs to A intersection B
= y belongs to A and y belongs to B
= y belongs to A
Therefore, B subset of A — (3) from (2) and (3) we get A=B. “ -
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
2 points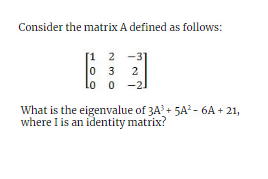 Correct
Correct
“The eigenvalues of A are 1, 3, –2 ( ∵ The given matrix is upper triangular)
Eigenvalues of A3 are 1, 27 and –8.
Eigenvalues of A2 are 1, 9 and 4.
Eigenvalues of A are 1, 3 and –2.
Eigenvalues of I are 1, 1 and 1.
∴ The eigenvalues of 3A3 + 5A2 – 6A + 2I.
First eigenvalue = 3(1) + 5(1) – 6(1) + 2(1) = 4
Second eigenvalue = 3(27) + 5(9) – 6(3) + 2(1) = 110
Third eigenvalue = 3(–8) + 5(4) – 6(–2) + 2(1) = 10
∴ The required eigenvalues are 4, 110, and 10. “Incorrect
“The eigenvalues of A are 1, 3, –2 ( ∵ The given matrix is upper triangular)
Eigenvalues of A3 are 1, 27 and –8.
Eigenvalues of A2 are 1, 9 and 4.
Eigenvalues of A are 1, 3 and –2.
Eigenvalues of I are 1, 1 and 1.
∴ The eigenvalues of 3A3 + 5A2 – 6A + 2I.
First eigenvalue = 3(1) + 5(1) – 6(1) + 2(1) = 4
Second eigenvalue = 3(27) + 5(9) – 6(3) + 2(1) = 110
Third eigenvalue = 3(–8) + 5(4) – 6(–2) + 2(1) = 10
∴ The required eigenvalues are 4, 110, and 10. “ -
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
2 pointsWhich one of the following is most affected by the presence of outliers in sample data?
Correct
“Let’s examine what can happen to a data set with outliers.
For the sample data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4
We find the following mean, median, mode, and standard deviation:
Mean = 2.58
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 1.08
If we add an outlier to the data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 400
The new values of our statistics are:
Mean = 35.38
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 114.74
Note: Outliers often has a significant effect on your mean and standard deviation. “Incorrect
“Let’s examine what can happen to a data set with outliers.
For the sample data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4
We find the following mean, median, mode, and standard deviation:
Mean = 2.58
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 1.08
If we add an outlier to the data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 400
The new values of our statistics are:
Mean = 35.38
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 114.74
Note: Outliers often has a significant effect on your mean and standard deviation. “ -
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
2 pointsWhat is the possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements?
Correct
“Step-1: To find number of reflexive relation we have standard formula is 2(n2-n)
Step-2: The possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements 2(n2-n) which is 220 for n=5. “Incorrect
“Step-1: To find number of reflexive relation we have standard formula is 2(n2-n)
Step-2: The possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements 2(n2-n) which is 220 for n=5. “ -
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
2 pointsIf a connected graph G has planar embedding with 4 faces and 4 vertices, then what will be the number of edges in G?
Correct
“Euler’s Formula for Planar Graphs:
For any(connected) planar graph with v vertices, e edges and faces, we have
V – E + F = 2
= 4 – E + 4 =2
E = 4 – 2 + 4
E = 6 “Incorrect
“Euler’s Formula for Planar Graphs:
For any(connected) planar graph with v vertices, e edges and faces, we have
V – E + F = 2
= 4 – E + 4 =2
E = 4 – 2 + 4
E = 6 “ -
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
2 points“Let P, Q and R be three atomic prepositional assertions, and
X : (P ∨ Q) → R
Y : (P → R) ∨ (Q → R)
Which one of the following is a tautology? “Correct
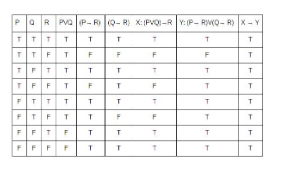 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
2 points“The probability that top and bottom cards of a randomly shuffled deck are both aces is:
Correct
“E 1 : First card being ace
E 2 : Last card being ace
Note that E 1 and E 2 are dependent events, i.e., probability of last card being ace if first is ace will be lesser than the probability of last card being ace if first card is not ace.
So, probability of first card being ace = 4/52
Probability of last card being ace given that first card is ace is,
P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 3/51
∴ P(E 1 and E 2 ) = P(E 1 ) ⋅ P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 4/52 * 3/51 “Incorrect
“E 1 : First card being ace
E 2 : Last card being ace
Note that E 1 and E 2 are dependent events, i.e., probability of last card being ace if first is ace will be lesser than the probability of last card being ace if first card is not ace.
So, probability of first card being ace = 4/52
Probability of last card being ace given that first card is ace is,
P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 3/51
∴ P(E 1 and E 2 ) = P(E 1 ) ⋅ P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 4/52 * 3/51 “ -
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
2 pointsThe relation {(1,2),(1,3)(3,1),(1,1),(3,3),(3,2),(1,4),(4,2),(3,4)} is
Correct
“Given set consists of elements a,b, and c.
The following conditions need to satisfy for each property.
a = a (reflexive property),
if a = b then b = a (symmetric property), and
if a = b and b = c then a = c (transitive property).
an asymmetric relation is a binary relation on a set X where:For all a and b in X, if a is related to b, then b is not related to a
The above relation is not reflexive because there is no ordered pairs (2,2) and (4,4)
The above relation is not Symmetric because if (1,2) present means the relation should consists of (2,1) but there is no such ordered pair in the relation.
Asymmetric property also invalid because of (1,3) and (3,1) ordered pairs. “Incorrect
“Given set consists of elements a,b, and c.
The following conditions need to satisfy for each property.
a = a (reflexive property),
if a = b then b = a (symmetric property), and
if a = b and b = c then a = c (transitive property).
an asymmetric relation is a binary relation on a set X where:For all a and b in X, if a is related to b, then b is not related to a
The above relation is not reflexive because there is no ordered pairs (2,2) and (4,4)
The above relation is not Symmetric because if (1,2) present means the relation should consists of (2,1) but there is no such ordered pair in the relation.
Asymmetric property also invalid because of (1,3) and (3,1) ordered pairs. “ -
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
2 pointsIf B is a Boolean algebra, then which of the following is true?
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is the dual of p ^ T≡ p:
Correct
Definition of dual!
Incorrect
Definition of dual!
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is tautology?
Correct
Draw Truth table to find Tautology
Incorrect
Draw Truth table to find Tautology
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
2 pointsThe proposition p v (~p ^ q) is
Correct
Draw TT or use simplification method
Incorrect
Draw TT or use simplification method
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
2 pointsGiven is Direct: p→q, what will be the contrapositive?
Correct
Use Definitions and deduce the statements
Incorrect
Use Definitions and deduce the statements
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
2 pointsIf (p v q) → r and ‘r’ is False(F) then result will be?
Correct
Draw TT or use simplification method
Incorrect
Draw TT or use simplification method
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
2 points“There are 40 questions and each question can be answered with any one of
four choices. Find the number of ways, in which they can be answered.”Correct
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
Incorrect
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
2 pointsThe number of ways of arranging the letters DEVVABDULL in a row:
Correct
Permutations!
Incorrect
Permutations!
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
2 pointsHow many 2 letter passwords can be made from {a, b, c}, if a letter can be used any number of times?
Correct
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
Incorrect
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
2 pointsIn a string of length 4, with distinct letters, how many substrings can be generated (other than null string)?
Correct
Use n(n+1)/2
Incorrect
Use n(n+1)/2
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
2 pointsHow many edges are possible in a forest with ‘n’ vertices and ‘k’ connected components?
Correct
Take examples and with definition try to solve
Incorrect
Take examples and with definition try to solve
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
2 pointsThe maximum number of edges in a bipartite graph on 15 vertices are?
Correct
“Possible combinations for total 15 vertices
1) 1 x 14= 14
2) 2 x 13= 26
3) 3 x 12 = 36
4) 4 x 11= 44
5) 5 x 10 = 50
6) 6 x 9= 54
7) 7 x 8= 56
so, max edges= 56 “Incorrect
“Possible combinations for total 15 vertices
1) 1 x 14= 14
2) 2 x 13= 26
3) 3 x 12 = 36
4) 4 x 11= 44
5) 5 x 10 = 50
6) 6 x 9= 54
7) 7 x 8= 56
so, max edges= 56 “ -
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
2 pointsThe sum of ‘Chromatic number’ and ‘Nullity’ for wheel graph with 8 vertices is________.
Correct
3+8=11
Incorrect
3+8=11
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
2 pointsA Connected planar graph having 15 vertices and 12 regions. Find the number of edges connecting the vertices in this graph.
Correct
” Euler’s formula: V= E-R+2
E= V+R-2
So, number of edges (E) = 15+12-2 = 25 “
Incorrect
” Euler’s formula: V= E-R+2
E= V+R-2
So, number of edges (E) = 15+12-2 = 25 “
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
2 pointsSuppose G= G (V, E) has 5 vertices, find the maximum number ‘m’ of edges in E if G is a multigraph
Correct
Edges can be any number
Incorrect
Edges can be any number
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
2 pointsLet X = {{}, {a}}. The power set of X is _______
Correct
Basics of Sets and power sets
Incorrect
Basics of Sets and power sets
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
2 pointsIdentify the correct statement:
Correct
Definitions
Incorrect
Definitions
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
2 points“Let X and Y be sets and X^C and Y^C denote the complements of Set X and Y.
The Set (X^C – Y^C) ∪(Y^C – X^C) ∪(X^C ∩ Y^C) is equal to ? Note : C means compliment here “
Correct
Solve usign boolean algebra simplification
Incorrect
Solve usign boolean algebra simplification
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is a group?
Correct
Check for group properties
Incorrect
Check for group properties
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
2 points“The sum 1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1! Can be written in the form 2a/ b! where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are positive integers.
The ordered pair (a, b) is”
Correct
“Sum=1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1!
Multiply and divided by 10! and you will get the answer “
Incorrect
“Sum=1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1!
Multiply and divided by 10! and you will get the answer “
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
2 pointsRange of f(x) = 2 + 6 sin x is___
Correct
Substitute sin values and solve for f(x)
Incorrect
Substitute sin values and solve for f(x)
- Next Quiz Daily at navclasses.in 12 PM
- Paper 2 Sunday at navclasses.in
Study Paper 1 Topics for Free Click Here
Get subscription for Complete Preparation NTA NET JRF: https://unacademy.com/subscribe/TEWDQ
use my referral code for 10% additional discount: NAVCLASSES
Search Navdeep Kaur and start watching ongoing courses
NTA NET Paper 1
Paper 2 CS Discrete Structures and Optimization Part 6
Quiz-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
Paper 1 Quiz helps u to Excel in NET JRF
Paper 1 All questions 2 Marks each
- Navdeep Kaur
- All the Best
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
Average marks Improve next time All the Best
-
Nice Keep it up, Stay Blessed
-
Awesome Great Marks, Keep doing
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
2 pointsLet L be a lattice. Then for every a and b in L which one of the following is correct?
Correct
“Distributive lattice is satisfies this condition aV(bVc)=(aVb)Vc
A distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other. “Incorrect
“Distributive lattice is satisfies this condition aV(bVc)=(aVb)Vc
A distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other. “ -
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
2 pointsIf A and B are sets and AUB = A∩B, then which of the following is correct?
Correct
“For this let x belongs to A implies x belongs to A U B
= x belongs to A intersection B
= x belongs to A and x Belongs to B
= x belongs to B
so A subset of B — (2)
Now we will let y belong to B which implies y belongs to A U B
= y belongs to A intersection B
= y belongs to A and y belongs to B
= y belongs to A
Therefore, B subset of A — (3) from (2) and (3) we get A=B. “Incorrect
“For this let x belongs to A implies x belongs to A U B
= x belongs to A intersection B
= x belongs to A and x Belongs to B
= x belongs to B
so A subset of B — (2)
Now we will let y belong to B which implies y belongs to A U B
= y belongs to A intersection B
= y belongs to A and y belongs to B
= y belongs to A
Therefore, B subset of A — (3) from (2) and (3) we get A=B. “ -
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
2 points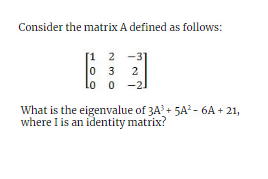 Correct
Correct
“The eigenvalues of A are 1, 3, –2 ( ∵ The given matrix is upper triangular)
Eigenvalues of A3 are 1, 27 and –8.
Eigenvalues of A2 are 1, 9 and 4.
Eigenvalues of A are 1, 3 and –2.
Eigenvalues of I are 1, 1 and 1.
∴ The eigenvalues of 3A3 + 5A2 – 6A + 2I.
First eigenvalue = 3(1) + 5(1) – 6(1) + 2(1) = 4
Second eigenvalue = 3(27) + 5(9) – 6(3) + 2(1) = 110
Third eigenvalue = 3(–8) + 5(4) – 6(–2) + 2(1) = 10
∴ The required eigenvalues are 4, 110, and 10. “Incorrect
“The eigenvalues of A are 1, 3, –2 ( ∵ The given matrix is upper triangular)
Eigenvalues of A3 are 1, 27 and –8.
Eigenvalues of A2 are 1, 9 and 4.
Eigenvalues of A are 1, 3 and –2.
Eigenvalues of I are 1, 1 and 1.
∴ The eigenvalues of 3A3 + 5A2 – 6A + 2I.
First eigenvalue = 3(1) + 5(1) – 6(1) + 2(1) = 4
Second eigenvalue = 3(27) + 5(9) – 6(3) + 2(1) = 110
Third eigenvalue = 3(–8) + 5(4) – 6(–2) + 2(1) = 10
∴ The required eigenvalues are 4, 110, and 10. “ -
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
2 pointsWhich one of the following is most affected by the presence of outliers in sample data?
Correct
“Let’s examine what can happen to a data set with outliers.
For the sample data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4
We find the following mean, median, mode, and standard deviation:
Mean = 2.58
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 1.08
If we add an outlier to the data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 400
The new values of our statistics are:
Mean = 35.38
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 114.74
Note: Outliers often has a significant effect on your mean and standard deviation. “Incorrect
“Let’s examine what can happen to a data set with outliers.
For the sample data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4
We find the following mean, median, mode, and standard deviation:
Mean = 2.58
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 1.08
If we add an outlier to the data set:
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 400
The new values of our statistics are:
Mean = 35.38
Median = 2.5
Mode = 2
Standard Deviation = 114.74
Note: Outliers often has a significant effect on your mean and standard deviation. “ -
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
2 pointsWhat is the possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements?
Correct
“Step-1: To find number of reflexive relation we have standard formula is 2(n2-n)
Step-2: The possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements 2(n2-n) which is 220 for n=5. “Incorrect
“Step-1: To find number of reflexive relation we have standard formula is 2(n2-n)
Step-2: The possible number of reflexive relations on a set of 5 elements 2(n2-n) which is 220 for n=5. “ -
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
2 pointsIf a connected graph G has planar embedding with 4 faces and 4 vertices, then what will be the number of edges in G?
Correct
“Euler’s Formula for Planar Graphs:
For any(connected) planar graph with v vertices, e edges and faces, we have
V – E + F = 2
= 4 – E + 4 =2
E = 4 – 2 + 4
E = 6 “Incorrect
“Euler’s Formula for Planar Graphs:
For any(connected) planar graph with v vertices, e edges and faces, we have
V – E + F = 2
= 4 – E + 4 =2
E = 4 – 2 + 4
E = 6 “ -
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
2 points“Let P, Q and R be three atomic prepositional assertions, and
X : (P ∨ Q) → R
Y : (P → R) ∨ (Q → R)
Which one of the following is a tautology? “Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
2 points“The probability that top and bottom cards of a randomly shuffled deck are both aces is:
Correct
“E 1 : First card being ace
E 2 : Last card being ace
Note that E 1 and E 2 are dependent events, i.e., probability of last card being ace if first is ace will be lesser than the probability of last card being ace if first card is not ace.
So, probability of first card being ace = 4/52
Probability of last card being ace given that first card is ace is,
P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 3/51
∴ P(E 1 and E 2 ) = P(E 1 ) ⋅ P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 4/52 * 3/51 “Incorrect
“E 1 : First card being ace
E 2 : Last card being ace
Note that E 1 and E 2 are dependent events, i.e., probability of last card being ace if first is ace will be lesser than the probability of last card being ace if first card is not ace.
So, probability of first card being ace = 4/52
Probability of last card being ace given that first card is ace is,
P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 3/51
∴ P(E 1 and E 2 ) = P(E 1 ) ⋅ P(E 2 / E 1 ) = 4/52 * 3/51 “ -
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
2 pointsThe relation {(1,2),(1,3)(3,1),(1,1),(3,3),(3,2),(1,4),(4,2),(3,4)} is
Correct
“Given set consists of elements a,b, and c.
The following conditions need to satisfy for each property.
a = a (reflexive property),
if a = b then b = a (symmetric property), and
if a = b and b = c then a = c (transitive property).
an asymmetric relation is a binary relation on a set X where:For all a and b in X, if a is related to b, then b is not related to a
The above relation is not reflexive because there is no ordered pairs (2,2) and (4,4)
The above relation is not Symmetric because if (1,2) present means the relation should consists of (2,1) but there is no such ordered pair in the relation.
Asymmetric property also invalid because of (1,3) and (3,1) ordered pairs. “Incorrect
“Given set consists of elements a,b, and c.
The following conditions need to satisfy for each property.
a = a (reflexive property),
if a = b then b = a (symmetric property), and
if a = b and b = c then a = c (transitive property).
an asymmetric relation is a binary relation on a set X where:For all a and b in X, if a is related to b, then b is not related to a
The above relation is not reflexive because there is no ordered pairs (2,2) and (4,4)
The above relation is not Symmetric because if (1,2) present means the relation should consists of (2,1) but there is no such ordered pair in the relation.
Asymmetric property also invalid because of (1,3) and (3,1) ordered pairs. “ -
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
2 pointsIf B is a Boolean algebra, then which of the following is true?
Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is the dual of p ^ T≡ p:
Correct
Definition of dual!
Incorrect
Definition of dual!
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is tautology?
Correct
Draw Truth table to find Tautology
Incorrect
Draw Truth table to find Tautology
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
2 pointsThe proposition p v (~p ^ q) is
Correct
Draw TT or use simplification method
Incorrect
Draw TT or use simplification method
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
2 pointsGiven is Direct: p→q, what will be the contrapositive?
Correct
Use Definitions and deduce the statements
Incorrect
Use Definitions and deduce the statements
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
2 pointsIf (p v q) → r and ‘r’ is False(F) then result will be?
Correct
Draw TT or use simplification method
Incorrect
Draw TT or use simplification method
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
2 points“There are 40 questions and each question can be answered with any one of
four choices. Find the number of ways, in which they can be answered.”Correct
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
Incorrect
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
2 pointsThe number of ways of arranging the letters DEVVABDULL in a row:
Correct
Permutations!
Incorrect
Permutations!
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
2 pointsHow many 2 letter passwords can be made from {a, b, c}, if a letter can be used any number of times?
Correct
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
Incorrect
Basics of Combinations and Permutations
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
2 pointsIn a string of length 4, with distinct letters, how many substrings can be generated (other than null string)?
Correct
Use n(n+1)/2
Incorrect
Use n(n+1)/2
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
2 pointsHow many edges are possible in a forest with ‘n’ vertices and ‘k’ connected components?
Correct
Take examples and with definition try to solve
Incorrect
Take examples and with definition try to solve
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
2 pointsThe maximum number of edges in a bipartite graph on 15 vertices are?
Correct
“Possible combinations for total 15 vertices
1) 1 x 14= 14
2) 2 x 13= 26
3) 3 x 12 = 36
4) 4 x 11= 44
5) 5 x 10 = 50
6) 6 x 9= 54
7) 7 x 8= 56
so, max edges= 56 “Incorrect
“Possible combinations for total 15 vertices
1) 1 x 14= 14
2) 2 x 13= 26
3) 3 x 12 = 36
4) 4 x 11= 44
5) 5 x 10 = 50
6) 6 x 9= 54
7) 7 x 8= 56
so, max edges= 56 “ -
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
2 pointsThe sum of ‘Chromatic number’ and ‘Nullity’ for wheel graph with 8 vertices is________.
Correct
3+8=11
Incorrect
3+8=11
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
2 pointsA Connected planar graph having 15 vertices and 12 regions. Find the number of edges connecting the vertices in this graph.
Correct
” Euler’s formula: V= E-R+2
E= V+R-2
So, number of edges (E) = 15+12-2 = 25 “
Incorrect
” Euler’s formula: V= E-R+2
E= V+R-2
So, number of edges (E) = 15+12-2 = 25 “
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
2 pointsSuppose G= G (V, E) has 5 vertices, find the maximum number ‘m’ of edges in E if G is a multigraph
Correct
Edges can be any number
Incorrect
Edges can be any number
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
2 pointsLet X = {{}, {a}}. The power set of X is _______
Correct
Basics of Sets and power sets
Incorrect
Basics of Sets and power sets
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
2 pointsIdentify the correct statement:
Correct
Definitions
Incorrect
Definitions
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
2 points“Let X and Y be sets and X^C and Y^C denote the complements of Set X and Y.
The Set (X^C – Y^C) ∪(Y^C – X^C) ∪(X^C ∩ Y^C) is equal to ? Note : C means compliment here “
Correct
Solve usign boolean algebra simplification
Incorrect
Solve usign boolean algebra simplification
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
2 pointsWhich of the following is a group?
Correct
Check for group properties
Incorrect
Check for group properties
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
2 points“The sum 1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1! Can be written in the form 2a/ b! where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are positive integers.
The ordered pair (a, b) is”
Correct
“Sum=1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1!
Multiply and divided by 10! and you will get the answer “
Incorrect
“Sum=1/ 1! 9! + 1/ 3!7! + 1 / 5! 5! + 1/ 7! 3! + 1/9! 1!
Multiply and divided by 10! and you will get the answer “
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
2 pointsRange of f(x) = 2 + 6 sin x is___
Correct
Substitute sin values and solve for f(x)
Incorrect
Substitute sin values and solve for f(x)






